4.2 Using the Descriptive Statistics in Excel to Obtain the Measures
Sample 1
- Go to
Data > Data Analysis. - Select
Descriptive Statisticsand clickOK.
Note: If Data Analysis does not appear in the Data menu, refer to the instructions in Lab 1 Getting Started with Excel how to make it available.
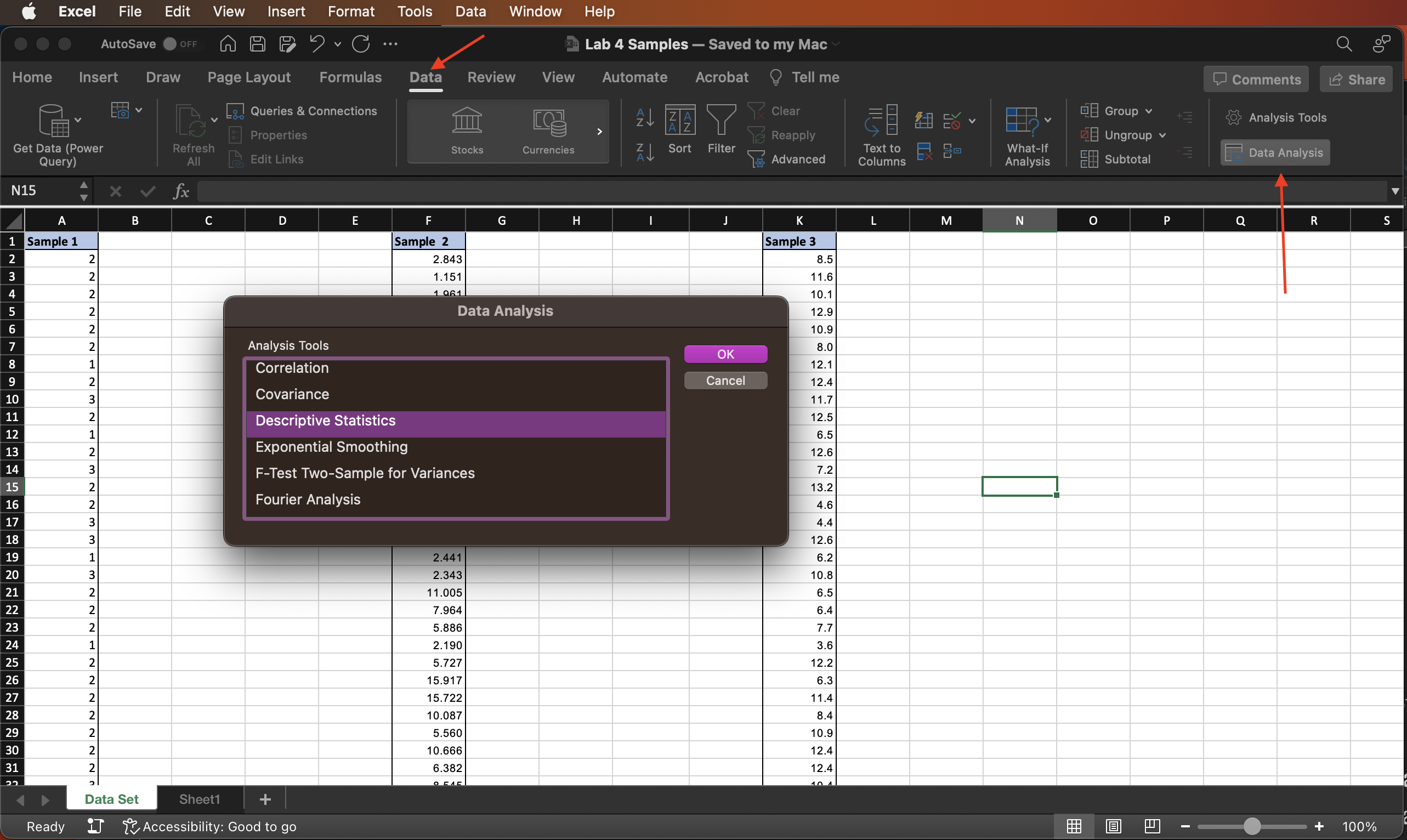
Figure 4.1: Data Analysis dialog window.
- The Descriptive Statistics window should appear. Complete the Descriptive Statistics window with the information needed from the data in Sample 1.
- The
Input Rangefor Sample 1 has cell address$A$2:$A$101(not including the label). If you include the label cell in the address, the address is$A$1:$A$101(the first cell address is different). You may want to fill in the input range by manually typing the address or by selecting the cells. - If the data values are stacked in a column, then check the options
Grouped by Columns. If they were entered into Rows instead, then you would select the rows option. - After you filled in the input range field, check or uncheck the box
Labels in the first rowaccording to what is in the input range. - Check the option
Output Rangeand select a cell in a blank area of your worksheet. 8.Check the optionSummary statistics. - Click
OK.
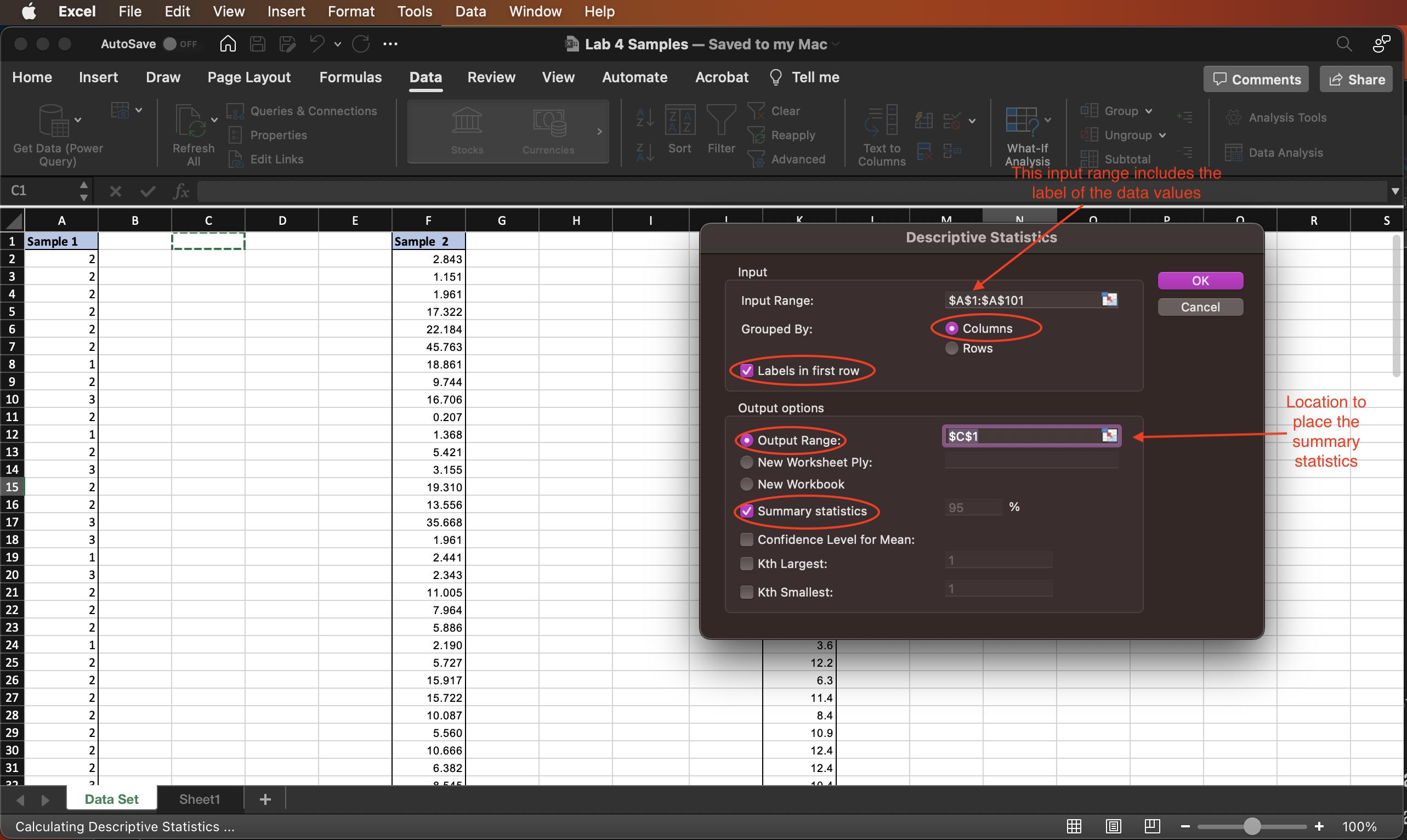
Figure 4.2: Descriptive Statistics dialog window.
These options give you the statistics of Sample 1 such as mean, median, standard deviation, and others.
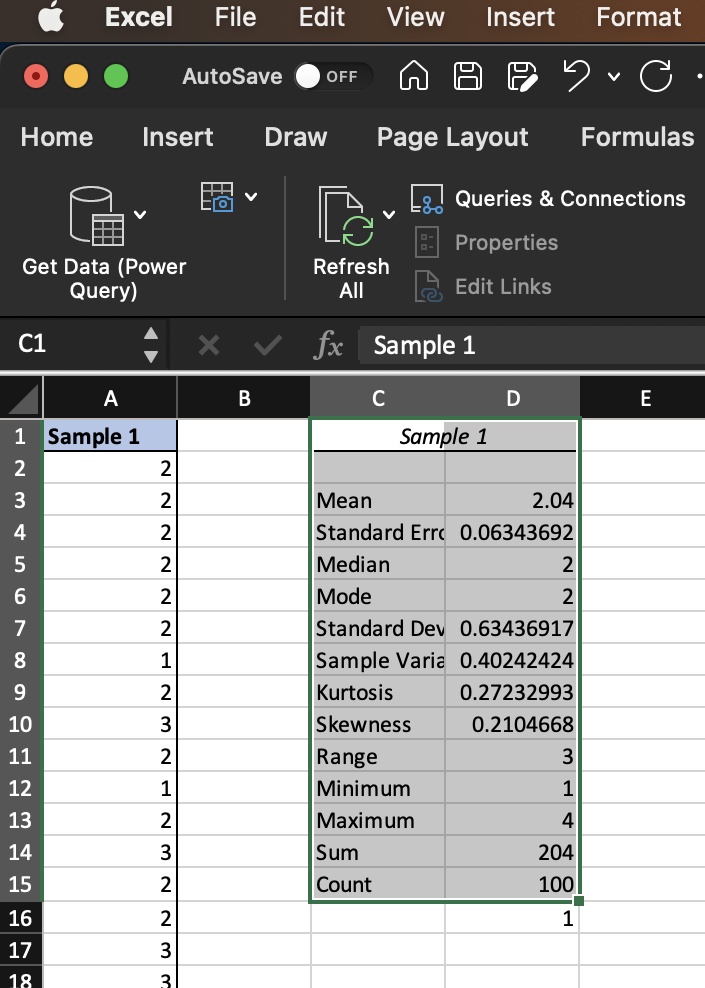
Figure 4.3: The resulting summary statistics for Sample 1.